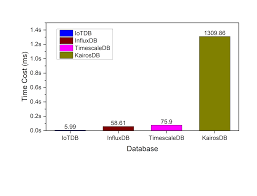
Time series databases (TSDBs) have become a cornerstone for monitoring, analytics, and real-time data applications. They allow businesses to track metrics over time, making it crucial for developers and analysts to retrieve data efficiently. However, when working with large volumes of time series data, poorly optimized queries can lead to slow performance, increased latency, and even system bottlenecks. In this article, we will explore how to optimize your API TSDB queries, particularly using Timecho, to enhance performance and ensure smoother data retrieval.
Understanding API TSDB Queries
An API TSDB query is a request sent to a time series database via an API to fetch data points over a period. These queries often include parameters such as time ranges, metrics, tags, aggregations, and filters. The efficiency of these queries directly affects the performance of applications that rely on real-time insights.
Timecho, a leading time series database platform, provides a robust API for handling large-scale metric data. Optimizing your API TSDB queries in Timecho ensures faster responses, lower resource usage, and better scalability for applications that need high-frequency data updates.
Choose the Right Time Range
One of the most common causes of slow API TSDB queries is requesting overly broad time ranges. Fetching years of data when only the last few hours are needed can overwhelm your database and slow down response times.
To optimize performance:
- Always define the smallest necessary time window.
- Use relative ranges like “last 24 hours” or “last 7 days” rather than retrieving all historical data.
- When working with large datasets, consider breaking queries into smaller intervals and aggregating results on the client side.
Timecho’s API supports precise time filtering, allowing developers to fetch exactly what is needed without unnecessary overhead.
Use Aggregation Functions Wisely
Aggregation functions like sum, average, max, and min can drastically reduce the amount of data returned in an API TSDB query. Instead of fetching thousands of raw data points, you can retrieve pre-aggregated metrics to gain insights quickly.
Tips for using aggregations effectively:
- Apply aggregation on the server side using Timecho’s built-in functions rather than performing calculations in the application.
- Use appropriate granularity; for instance, if hourly trends are sufficient, avoid retrieving minute-level data.
- Combine multiple aggregations in one query where possible to reduce the number of API calls.
This approach minimizes data transfer and processing time, leading to significantly improved query performance.
Filter Data Using Tags and Labels
Time series databases often store multiple metrics across various sources. Retrieving all metrics without filtering can lead to unnecessarily heavy API TSDB queries. Tags and labels allow you to narrow down your data selection effectively.
For example, in Timecho:
- Use tags like
host,region, orserviceto limit results. - Combine multiple filters logically to avoid fetching unrelated data.
- Avoid wildcard queries on high-cardinality tags, as these can increase query complexity and slow down response times.
Properly filtered queries ensure that only the necessary subset of data is retrieved, making your API calls faster and more efficient.
Limit the Number of Data Points Returned
Many API TSDB queries fail to consider the sheer volume of points returned. Pulling millions of points in a single request can overwhelm both the database and the client application.
To address this:
- Use Timecho’s
limitparameter to restrict the number of points returned. - Consider downsampling data when high-resolution information is unnecessary.
- Retrieve data in batches for long time periods, then merge or process it in your application.
This practice prevents timeouts, reduces memory usage, and ensures a smooth experience for end-users.
Cache Frequently Accessed Data
Caching is an often-overlooked optimization for API TSDB queries. If the same metrics are requested frequently, storing the results temporarily can save repeated database calls.
Best practices for caching:
- Cache aggregated results rather than raw data points for efficiency.
- Use a cache with expiration times aligned with your data update frequency.
- Implement client-side caching for dashboard applications where repeated queries occur.
Timecho’s API is designed to handle high-volume queries efficiently, but combining it with caching further reduces load and improves performance.
Optimize Query Structure
The structure of your API TSDB query can greatly influence execution speed. Inefficient queries with unnecessary joins, complex filters, or repeated functions can slow down response times.
Optimization strategies include:
- Simplify queries by removing redundant filters or transformations.
- Consolidate multiple queries into one where possible using batch requests.
- Use Timecho’s query syntax to leverage built-in functions instead of performing operations post-fetch.
Well-structured queries not only run faster but also reduce the computational load on your Timecho instance.
Monitor and Analyze Query Performance
Continuous monitoring of API queries is essential for maintaining performance. Timecho provides tools to track query execution times, resource consumption, and error rates. By analyzing these metrics, you can identify bottlenecks and refine your API TSDB queries over time.
Consider implementing:
- Logging of slow queries to pinpoint inefficiencies.
- Metrics dashboards that show API response times and query volumes.
- Alerts for abnormal query latency, which can indicate database strain or suboptimal queries.
Monitoring ensures that optimizations are effective and helps maintain a high-performance system as data volumes grow.
Use Pagination for Large Data Sets
When working with extensive datasets, avoid retrieving all points in a single query. Timecho supports pagination, allowing you to fetch data in manageable chunks. This reduces network overhead and prevents timeouts.
Pagination best practices:
- Combine pagination with time-range filters to balance data retrieval.
- Use incremental loading for dashboards to improve user experience.
- Ensure consistency by using stable sort keys or timestamps.
This method keeps API calls responsive even under heavy loads.
Implement Rate Limiting and Throttling
To maintain stable performance, consider implementing rate limiting and throttling for your API TSDB queries. This prevents overwhelming your Timecho instance during peak usage.
Strategies include:
- Setting maximum query rates per client or service.
- Queueing or delaying non-critical queries during high traffic periods.
- Monitoring API usage to adjust limits dynamically.
Rate limiting protects your infrastructure and ensures consistent performance for all users.
Conclusion
Optimizing API TSDB queries is critical for maximizing performance and ensuring that applications relying on time series data remain responsive. By carefully selecting time ranges, using aggregation, filtering effectively, limiting data points, caching results, and structuring queries efficiently, developers can significantly improve API performance.
Timecho provides a powerful platform for handling time series data, and leveraging these optimization techniques ensures that your API interactions are fast, efficient, and scalable. Regular monitoring and ongoing adjustments to queries keep your system performing at its best, even as data grows and demands increase. With these strategies, you can unlock the full potential of your time series database and deliver real-time insights without compromising speed or reliability.